Shell -
It is a Command line Interface that will interpret our commands. It executes each and every command line by line.
Since everything in Linux is a File(even the commands) how will the Operating System know where is the file for a command and How to convert these instructions?
-> Shell will do all these things for you.
pwd, ls, cd
Print working directory(pwd) prints the working directory starting from the root. Its stored inside a environment variable($PWD).
ls gives us a list of contents (Files, Directories) of the current directory. ls will give you list of contents(Files, Directories) of that particular directory.
cd is used to change directory. cd will take you inside that directory. cd .. will bring you out of the current directory.
mkdir, rm, rmdir
mkdir is Used to create a directory. -p is used when we’ve to create a directory inside a directory.
rm is used to delete a file, rmdir is used to delete a directory.
grep
grep stands for Global Regular Expression Print. Its used to search files by characters. Its one of the most commonly used commands.
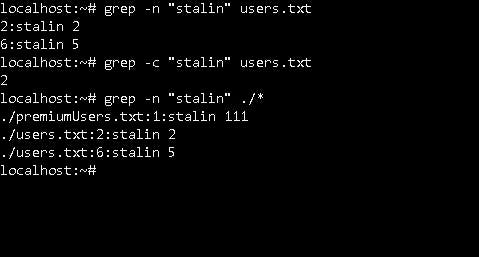
- Here, we’re searching for the word ‘stalin’ in the file users.txt. -n is used for getting the line no. and -c is used to get the count. ./* will get us all the matches in the current directory.
Whatis, man
Whatis gives us a description of the command.
man command gives us a manual of the specified command. This manual will have different flags which we can use with the command. Its like a documentation.
less, Pipe
It opens output in a separate window so that the terminal doesn’t get messed up. Its used when the output will be long.
Pipe takes output of 1 command(left side) and gives it as a input to another command on right side.
Eg. ls -la /etc | less
- It gives us list of contents(Files, directories) in /etc folder in a long list with hidden files is given as input to less command. less opens it in a separate window which allows us to manage this long list efficiently.
wc, head, tail sort, tr, uniq
wc -> Gives no. of lines, words, bytes in a file.
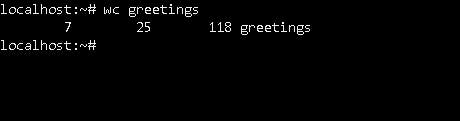
Here is 7 no. of lines, 25 is no. of words and 118 is no. of bytes of the file, greetings is the file name.
head -> It gives us first 10 lines of a file by default. If you want more lines then use head -n(no. of lines) file name.
tail -> It gives us last 10 lines of a file by default. If you want more lines then use head -n(no. of lines) file name.
sort -> sorts file in a particular order. tr -> Translates / Changes contents of a file. uniq -> Used to check for duplicate values.
chmod, umask
Using chmod we can change / Modify permissions. Plus(+) for Adding permissions, minus(-) for Deleting permissions.
We can also use numbers for changing permissions. 1 is for execute, 2 is for write and 4 is for read permission. 5(4+1) is for read and write. 7(4+1+3) is for reading, write, execute permissions. 6(4+2) is for read and execute.
umask is used to change Default Permissions.

